设计模式学习笔记原型模式以及深浅拷贝的区别
原型模式也是创建对象的一种方式,它一般用在这样的场景:系统中存在大量相同或相似对象的创建问题,如果用传统的构造函数来创建对象,会比较复杂而且耗费资源。这个时候使用原型模式的克隆方式,能够节省不少时间。比如Java 类中提供的Object clone()就是原型模式的应用。
一、原型模式介绍
原型设计模式(Prototype Design Pattern)指用一个已经创建的实例作为原型,通过复制该原型对象来创建一个和原型相同或相似的新对象。在Java语言中就存在克隆的方式,比如浅拷贝和深拷贝。
对于一般的对象创建,本身不会花费太多的资源,但是对于负责的对象,比如对象的数据需要经过复杂的计算才能得到(比如排序、计算哈希值),抑或是需要从 RPC、网络、数据库、文件系统等非常慢速的IO中读取,这个时候就可以利用原型模式从其他对象直接拷贝,从而减少资源的消耗。
二、原型模式的实现
在Java中原型模式的实现方式就是深拷贝和浅拷贝,下面来谈谈深拷贝和浅拷贝的区别
2.1 深拷贝和浅拷贝
2.1.1 浅拷贝
浅拷贝(Shadow Clone)是把原型对象中的成员变量为值类型的属性都复制给克隆对象,将为引用类的引用地址复制给克隆对象:
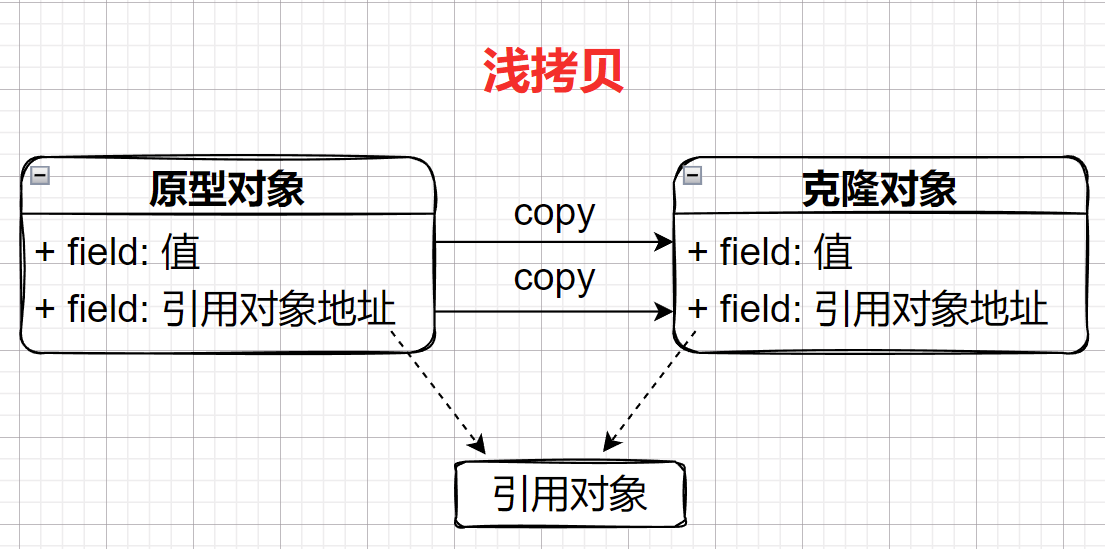
实现代码如下:
//实现Cloneable接口 public class ShadowCopy implements Cloneable{ private String name; private int id; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public ShadowCopy(String name, int id) { this.name = name; this.id = id; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } } //调用测试 public class PrototypeTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { ShadowCopy shadowCopy = new ShadowCopy("ethan", 01); ShadowCopy copy = (ShadowCopy) shadowCopy.clone(); System.out.println("name:" + copy.getName() + " " + "id:" + copy.getId()); System.out.println(copy == shadowCopy); } }从最后的测试结果copy == shadowCopy显示为false,说明为浅拷贝。我们再看看深拷贝:
2.1.2 深拷贝
深拷贝(Deep Clone)是将原型对象中的所有对象,无论值类型还是引用类型,都复制一份给拷贝对象:
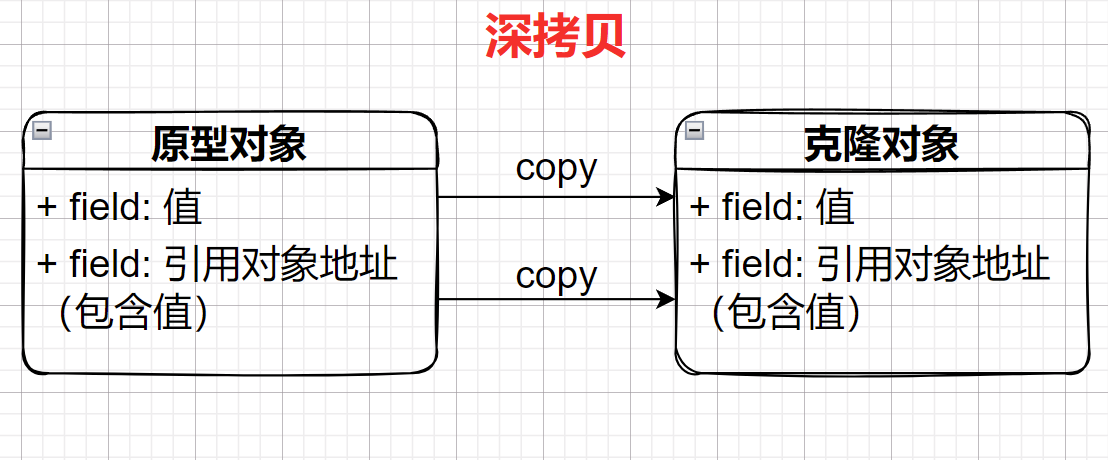
那么深拷贝该如何实现?而且前面我们发现,在拷贝时为何需要重写Object的clone方法?先来看看其源码,发现clone方法是一个本地方法:
/** * Creates and returns a copy of this object. The precise meaning * of "copy" may depend on the class of the object. The general * intent is that, for any object {@code x}, the expression: * <blockquote> * <pre> * x.clone() != x</pre></blockquote> * will be true, and that the expression: * <blockquote> * <pre> * x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()</pre></blockquote> * will be {@code true}, but these are not absolute requirements. * While it is typically the case that: * <blockquote> * <pre> * x.clone().equals(x)</pre></blockquote> * will be {@code true}, this is not an absolute requirement. * <p> * By convention, the returned object should be obtained by calling * {@code super.clone}. If a class and all of its superclasses (except * {@code Object}) obey this convention, it will be the case that * {@code x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()}. * <p> * By convention, the object returned by this method should be independent * of this object (which is being cloned). To achieve this independence, * it may be necessary to modify one or more fields of the object returned * by {@code super.clone} before returning it. Typically, this means * copying any mutable objects that comprise the internal "deep structure" * of the object being cloned and replacing the references to these * objects with references to the copies. If a class contains only * primitive fields or references to immutable objects, then it is usually * the case that no fields in the object returned by {@code super.clone} * need to be modified. * <p> * The method {@code clone} for class {@code Object} performs a * specific cloning operation. First, if the class of this object does * not implement the interface {@code Cloneable}, then a * {@code CloneNotSupportedException} is thrown. Note that all arrays * are considered to implement the interface {@code Cloneable} and that * the return type of the {@code clone} method of an array type {@code T[]} * is {@code T[]} where T is any reference or primitive type. * Otherwise, this method creates a new instance of the class of this * object and initializes all its fields with exactly the contents of * the corresponding fields of this object, as if by assignment; the * contents of the fields are not themselves cloned. Thus, this method * performs a "shallow copy" of this object, not a "deep copy" operation. * <p> * The class {@code Object} does not itself implement the interface * {@code Cloneable}, so calling the {@code clone} method on an object * whose class is {@code Object} will result in throwing an * exception at run time. * * @return a clone of this instance. * @throws CloneNotSupportedException if the object's class does not * support the {@code Cloneable} interface. Subclasses * that override the {@code clone} method can also * throw this exception to indicate that an instance cannot * be cloned. * @see java.lang.Cloneable */ protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;从注释可以知道,对于所有对象来说:
x.clone()!=x应当返回true,因为克隆对象不能和原对象是同一个对象x.clone().getClass()==x.getClass()应当返回true,因为克隆对象和原对象的类型是相同的x.clone().equals(x)应当返回true,因为使用equals方法比较时,其值都是相同的
Java 实现拷贝主要有两个步骤:一是实现Cloneable空接口,二是重写Object的Clone方法后再调用父类的克隆方法super.clone(),那为何这样做?
拷贝功能不是一个常用的功能,因此在对象需要时实现即可,这样比较合理,而且在Java语言中一个类也可以实现多个接口。对于调用clone方法,因为该方法语义的特殊性,所以要有JVM的直接支持,而clone方法就是这个调用接口,一旦有类调用这个方法,就可以实现拷贝功能了。
2.1.3 深拷贝的实现方式
深拷贝的实现方式有很多种,大体上有这样几种:
1.所有对象都实现深拷贝
这种方式需要让类中所有引用对象都实现拷贝,从而实现类的深拷贝,代码如下:
public class CloneExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { // 创建被赋值对象 Address address = new Address(110, "北京"); People p1 = new People(1, "Java", address); // 克隆 p1 对象 People p2 = p1.clone(); // 修改原型对象 p1.getAddress().setCity("西安"); // 输出 p1 和 p2 地址信息 System.out.println("p1:" + p1.getAddress().getCity() + " p2:" + p2.getAddress().getCity()); } /** * 用户类 */ static class People implements Cloneable { private Integer id; private String name; private Address address; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Address getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(Address address) { this.address = address; } public People(Integer id, String name, Address address) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.address = address; } /** * 重写 clone 方法 * @throws CloneNotSupportedException */ @Override protected People clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { People people = (People) super.clone(); people.setAddress(this.address.clone()); // 引用类型克隆赋值 return people; } } /** * 地址类 */ static class Address implements Cloneable { private Integer id; private String city; public Address(Integer id, String city) { this.id = id; this.city = city; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } /** * 重写 clone 方法 * @throws CloneNotSupportedException */ @Override protected Address clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return (Address) super.clone(); } } }2.通过构造方法实现深拷贝
如果构造方法的参数为基本数据类型或者字符串类型,直接进行赋值即可,如果是对象类型,则需要重新 new 一个对象,实现代码如下:
public class CloneExample2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Address address = new Address(100, "北京"); People people1 = new People(1, "ethan", address); People people2 = new People(people1.getId(), people1.getName(), new Address(people1.getAddress().getId(), people1.getAddress().getCity())); } static class People { private Integer id; private String name; private Address address; public People(Integer id, String name, Address address) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.address = address; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Address getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(Address address) { this.address = address; } } static class Address { private Integer id; private String city; public Address(Integer id, String city) { this.id = id; this.city = city; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } } }3.通过字节流实现深拷贝
可以通过 JDK 自带的字节流实现深拷贝的方式,是先将要原型对象写入到内存中的字节流,然后再从这个字节流中读出刚刚存储的信息,来作为一个新的对象返回,那么这个克隆对象和原型对象就不存在任何地址上的共享,实现代码如下:
public class CloneExample3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Address address = new Address(100, "北京"); People people1 = new People(1, "ethan", address); //字节流拷贝对象 People people2 = StreamClone.clone(people1); } static class StreamClone { public static <T extends Serializable> T clone(People obj) { T cloneObj = null; try { //写入字节流 ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream); objectOutputStream.writeObject(obj); objectOutputStream.close(); //分配内存,写入原始对象并生成新对象 ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray()); ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(byteArrayInputStream); //返回生成的新对象 cloneObj = (T) objectInputStream.readObject(); objectInputStream.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return cloneObj; } } static class People implements Serializable { private Integer id; private String name; private Address address; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Address getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(Address address) { this.address = address; } public People(Integer id, String name, Address address) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.address = address; } } static class Address implements Serializable { private Integer id; private String city; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public Address(Integer id, String city) { this.id = id; this.city = city; } } }在利用字节流进行拷贝时,要注意每个对象必须实现Serizlizable接口,标识自己可以被序列化,否则就会抛出(java.io.NotSerizlizableException)异常。
4.通过Apache Commons Lang实现深拷贝
相对于方法3,这个方法可以直接调用,实现代码如下:
People people2 = (People)SerizlizationUtils.clone(people1); //其他部分和方法3相同,省略5.通过JSON工具类实现深拷贝
Gson gson = new Gson(); People people2 = gson.fromJson(gson.toJson(people1), People.class);在该方法中,不需要对People和Address类进行标识序列化。使用JSON 工具类会先把对象转化成字符串,然后再从字符串转化成新的对象,因此不会和原型对象有关联。从而实现了深拷贝,其他类似的 JSON 工具类的实现方式也是如此。
三、总结
原型模式在 Java 中主要有两种实现方式:深拷贝和浅拷贝,两者区别是深拷贝会复制引用对象,浅拷贝只会复制引用对象的地址。深拷贝相对于浅拷贝更加耗时和资源。
为何有深拷贝的存在呢?因为对于可变对象来说,浅拷贝对于引用对象的地址拷贝会带来修改风险。所以在可变对象的场景下,尽量还是选择深拷贝的方式进行复制。
参考资料
https://time.geekbang.org/column/article/200786
《Java 重学设计模式》
https://kaiwu.lagou.com/course/courseInfo.htm?courseId=59#/detail/pc?id=1767
热门文章
- 「2月23日」最高速度22.3M/S,2025年V2ray/SSR/Shadowrocket/Clash/HiddifyNext每天更新免费节点订阅链接
- 设计模式学习笔记原型模式以及深浅拷贝的区别
- 「12月29日」最高速度18.9M/S,2024年Clash/V2ray/Shadowrocket/SSR/HiddifyNext每天更新免费节点订阅链接
- 猫瘟***多少钱(猫瘟***需要多少钱)
- 动物医院规模多大合适(动物医院挣钱吗)
- 动物疫苗行业的毛利润率 动物疫苗行业的毛利润率是多少
- ElasticSearch(五) 整合Spring-data-elasticsearch
- react实战系列起步(mockjs、第一个模块、docusaurus)
- 动物疫苗的正确使用方法图片大全集(动物疫苗的正确使用方法图片大全集视频)
- 动物疫苗监管部门投诉电话是多少(动物疫苗监管部门投诉电话是多少号)